前言
最近一直在研究人工智能,包括处理一些图片或者视频的视觉目标检测,接触了 YOLO ,索性就好好研究一下,在这里记录一下。
背景
要想微调 YOLO 首先要有数据,官方网站给出了微调代码,也提供了一些数据,但是毕竟不同的需求需要的数据不同,在这里将记录一下如何制作微调所需的数据。这里使用 labelme 标注软件,他生成的数据是 json 格式,还需要转化为 YOLO 需要的 TXT 格式。
labelme 安装
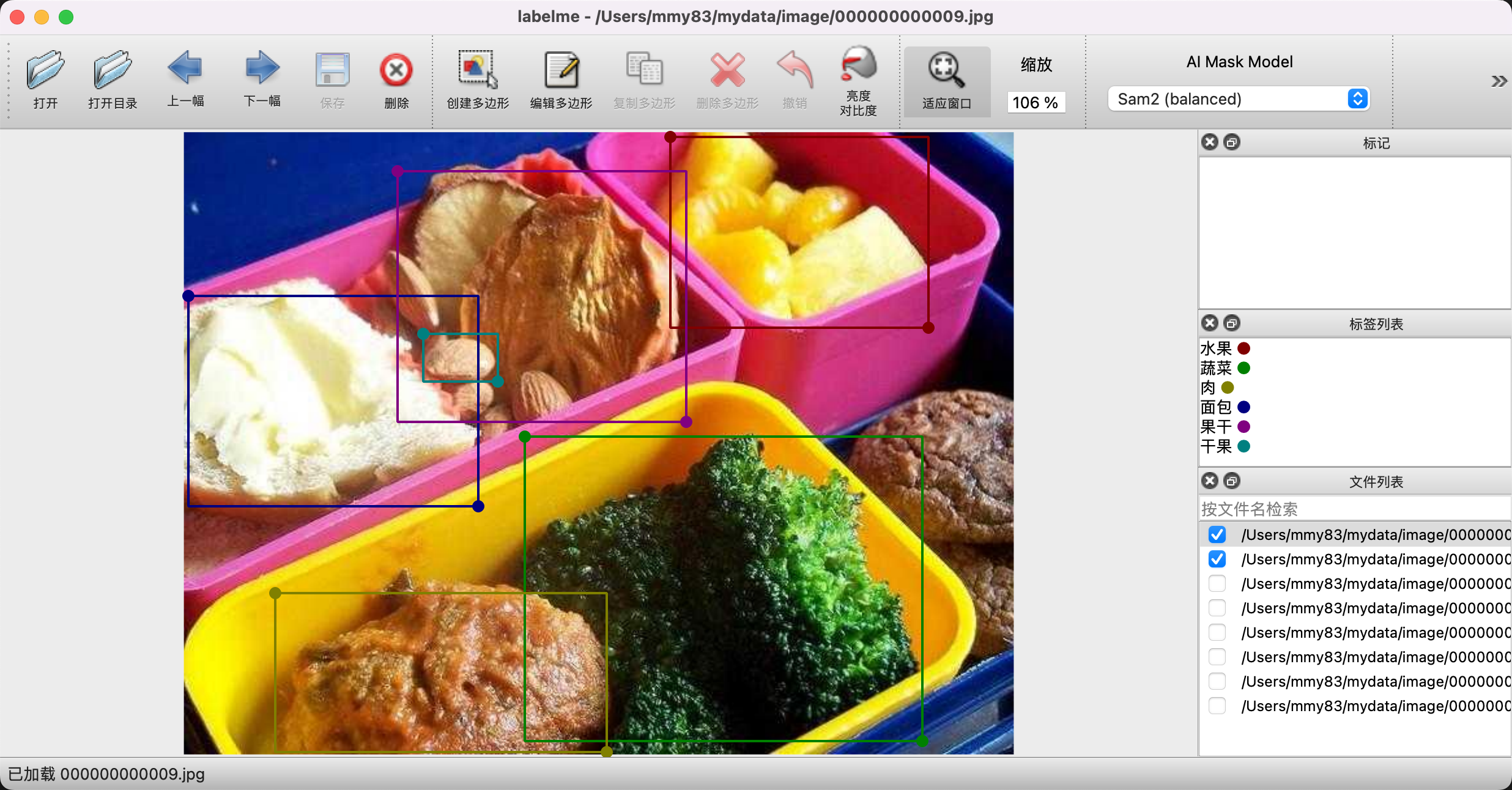
labelme 是一款开源的 python+Qt 开发的一款功能比较强大的图片标注软件,支持多边形、矩形、原型等标注方式。安装和使用都很简单。
开源地址:https://github.com/wkentaro/labelme
1
2
3
4
5
# 安装
pip install labelme
# 启动
labelme
注:
有一款 labelimg的,也是python的,但是我本地使用总报错。
有一款web版本的标注系统 https://github.com/cvat-ai/cvat
labelme 的数据格式
labelme 默认的数据格式是一个和图片同名的 json 文件。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
{
"version": "5.8.1",
"flags": {},
"shapes": [
{
"label": "长颈鹿",
"points": [
[
375.88235294117646,
68.0420168067227
],
[
594.3697478991597,
357.11764705882354
]
],
"group_id": null,
"description": "",
"shape_type": "rectangle",
"flags": {},
"mask": null
}
],
"imagePath": "000000000025.jpg",
"imageData": "这里是图片文件的base64",
"imageHeight": 426,
"imageWidth": 640
}
说明:
version:labelme 软件版本号
flags:一个可选的标志字典,通常为空
shapes:一个列表,包含每个标注的详细信息
label:这个标注的标签名。
points:一个数字,包含标注的点的坐标。对于多边形,每个点用 (x,y) 表示;对于矩形,通常有两个点:左上角和右下角。
group_id:一个可选的组ID,用于标记同一组的多个形状。
description:一个可选的描述,用于描述这个标注
shape_type:形状类型,如:polygon(多边形)、rectangle(矩形),circle(圆形)等。
flags:可选的标志字典,通常为空
mask:遮罩,AI Mask Model 功能使用,一般为null。
imagePath:原始图像的路径或名称。
imageData:图像数据的 base64 编码字符串。这个字段可以为空,如果有图像路径信息的话。
imageHeight:图像的高度。
imageWidth图像的宽度。
YOLO要求的数据格式
用用来微调 YOLO ,据需要知道 YOLO 需要的数据格式。YOLO 使用一种简单的 TXT 文本格式来存储每个图像的标注数据。
每个图像对应一个文本文件。
文本文件和图片文件同名,但文件后缀是 .txt.
每个文本文件包含一行或多行,每一行代表一个物体的标注。
每行包含的信息个数为:
<class_id> <x_center> <y_center> <width> <height>(相邻数据用英文空格间隔)。-
:类别ID,从0开始。 -
:边界框中心的 x 坐标,归一化到图像宽度(值在 0 到 1 之间)。 -
:边界框中心的 y 坐标,归一化到图像高度(值在 0 到 1 之间)。 <width>:边界框的宽度,归一化到图像宽度(值在 0 到 1 之间)。
- <height>:边界框的高度,归一化到图像高度(值在 0 到 1 之间)。
-
格式转化
知道上面的格式了,我们自然也就好处理,只要通过代码直接将 json 文件改写成 YOLO 需要的 TXT 文件即可。
手动转化
单个文件转化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
import json
import os
# 定义标签映射
label_map = {
"car": 0,
"bus": 1
}
def convert_labelme_to_yolo(json_path, output_dir):
with open(json_path, 'r') as f:
labelme_data = json.load(f)
image_width = labelme_data['imageWidth']
image_height = labelme_data['imageHeight']
yolo_annotations = []
for shape in labelme_data['shapes']:
label = shape['label']
if label not in label_map:
continue # 忽略未定义的标签
class_id = label_map[label]
points = shape['points']
if shape['shape_type'] == 'rectangle':
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
elif shape['shape_type'] == 'polygon':
x1, y1 = min(point[0] for point in points), min(point[1] for point in points)
x2, y2 = max(point[0] for point in points), max(point[1] for point in points)
else:
continue # 其他类型不处理
x_center = (x1 + x2) / 2.0 / image_width
y_center = (y1 + y2) / 2.0 / image_height
width = (x2 - x1) / image_width
height = (y2 - y1) / image_height
yolo_annotations.append(f"{class_id} {x_center} {y_center} {width} {height}")
output_file = os.path.join(output_dir, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(json_path))[0] + '.txt')
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(yolo_annotations))
# 示例使用
convert_labelme_to_yolo('/path/to/labelme_file.json', '/path/to/output_dir')
批量转化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
import json
import os
# 定义标签映射
label_map = {
"car": 0,
"bus": 1
}
def convert_labelme_to_yolo(json_path, output_dir):
with open(json_path, 'r') as f:
labelme_data = json.load(f)
image_width = labelme_data['imageWidth']
image_height = labelme_data['imageHeight']
yolo_annotations = []
for shape in labelme_data['shapes']:
label = shape['label']
if label not in label_map:
continue # 忽略未定义的标签
class_id = label_map[label]
points = shape['points']
if shape['shape_type'] == 'rectangle':
(x1, y1), (x2, y2) = points
elif shape['shape_type'] == 'polygon':
x1, y1 = min(point[0] for point in points), min(point[1] for point in points)
x2, y2 = max(point[0] for point in points), max(point[1] for point in points)
else:
continue # 其他类型不处理
x_center = (x1 + x2) / 2.0 / image_width
y_center = (y1 + y2) / 2.0 / image_height
width = (x2 - x1) / image_width
height = (y2 - y1) / image_height
yolo_annotations.append(f"{class_id} {x_center} {y_center} {width} {height}")
output_file = os.path.join(output_dir, os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(json_path))[0] + '.txt')
with open(output_file, 'w') as f:
f.write('\n'.join(yolo_annotations))
def process_folder(input_folder, output_folder):
# 创建输出文件夹(如果不存在)
os.makedirs(output_folder, exist_ok=True)
# 处理输入文件夹中的每个 JSON 文件
for filename in os.listdir(input_folder):
if filename.endswith(".json"):
json_path = os.path.join(input_folder, filename)
convert_labelme_to_yolo(json_path, output_folder)
# 示例使用
input_folder = "/mnt/data/buffer_nails_all"
output_folder = "/mnt/data/yolo_labels"
process_folder(input_folder, output_folder)
# 列出输出文件夹中的文件以确认
os.listdir(output_folder)
说明文件
光有上面的数据还不行,还需要一个对这个数据进行说明的文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
path: dataset/coco8 # 数据集所在目录
train: images/train # 训练集目录(不需要加上path的值),表示的具体路径:coco8/images/train
val: images/val # 验证集目录
test: images/test # 测试集目录
# 标注的分类,按序号依次往下排,注意这个是 json 文件中的标注信息中的 label。需要和 TXT 对应好,否识别就会错乱,这个其实就是代码中的 label_map,这样似乎有些麻烦,可以通过改写代码一步完成。
names:
0: person
1: bicycle
2: car
3: motorcycle
# Download script/URL (optional)
download: https://github.com/ultralytics/assets/releases/download/v0.0.0/coco8.zip # 数据集下载地址,非必须,也可以是python脚本
自动转化
上面的方式就算使用代码也很麻烦,其实还要一个转化工具可以一步到位。其实原理是一样的。
安装
1
pip install labelme2yolo
执行
1
labelme2yolo --json_dir ./ --val_size 0.25 --test_size 0.25
参数说明:
–json_dir:labelme软件标注后的 json 路径。
–val_size:验证集的大小(总数据集的0.25)。
–test_size:测试集的大小(总数据集的0.25)。
-d, –json_dir
labelme软件标注后的 json 路径。 –val_size
验证集的大小(总数据集的0.25)。 (0.0 到 1.0) [默认: 0.2]。 –test_size
测试集的大小(总数据集的0.25)。 (0.0 到 1.0) [默认: 0]. –output_format
输出的yolo注解: 'bbox' or 'polygon' [默认: bbox] [别名: format] [可选值: polygon(多边形), bbox]。YOLO 中的bbox的格式是(x,y,w,h),也就是给bbox的中心点坐标和长宽,为了方便训练,这四个值都是要做标准化处理,也就是除以原图的尺寸,它们的取值都是在0~1之间。也就是上面说的 TXT 每一行的格式。 –seed 随机混洗种子 [默认: 42].
-h, –help 帮助
-V, –version 版本
注意:
工具中只有验证集大小和测试集大小,剩下的是训练集的大小,也就不需要指定了。
生成的数据集的目录结构,包含说明文件:
1
2
3
4
5
/path/to/labelme_json_dir/YOLODataset/labels/train/
/path/to/labelme_json_dir/YOLODataset/labels/val/
/path/to/labelme_json_dir/YOLODataset/images/train/
/path/to/labelme_json_dir/YOLODataset/images/val/
/path/to/labelme_json_dir/YOLODataset/dataset.yaml